Influence Of Low Speed On The Quality Of Parts In High Pressure Die Casting
- Delia Wu/CAMEL
- Sep 16, 2020
- 3 min read
Updated: Jul 27, 2021
Abstract: High-pressure die casting is an important process for forming non-ferrous metal structures. The production elements of die casting are composed of a die casting machine, die casting mold, die-casting process, and die casting alloy. Low speed (hereinafter referred to as low-speed) is one of the key parameters of the die casting process. The low-speed setting has a more important effect on the quality of die-casting parts. This article will verify the impact of the low speed of die casting on the quality of parts while ensuring other parameters are not changed.
Keywords: Die casting process; Low speed; Die casting parts.
1.Filling effect of casting at low pressure of 0.2m/s

Figure 1.1 The filling state of the low-speed 0.2m/s shot sleeve
① The filling of aluminum liquid is relatively stable, and no obvious entrained air is seen.

Figure 1.2 Temperature distribution after low-speed 0.2m / s castings is filled.
② The overall temperature of the casting is about 570°C, which is slightly lower than the liquidus line of the A380 material at 574.4°C. The risk of defects such as the cold lab and flow marks on the surface is higher.
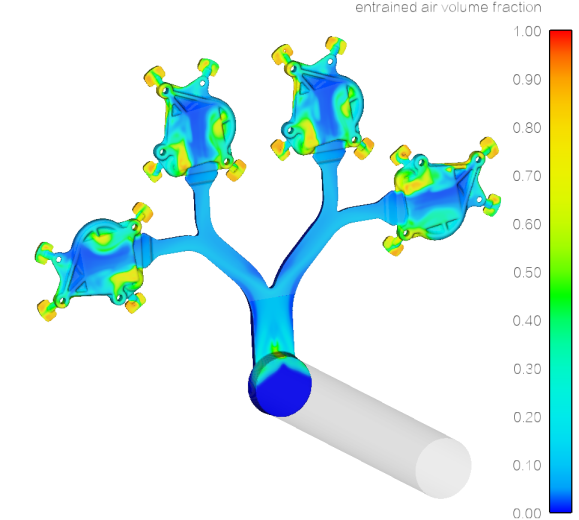
Figure 1.3 Entrained air volume fraction after low-speed 0.2m / s casting is filled.
③ Entrained air is basically discharged into the overflow, and the risk of defects such as porosity and surface bubbles in the casting is low.
2.Filling effect of casting at low-speed 0.3m/s

Figure 2.1 Filling state of the low-speed 0.3m/s shot sleeve.
① Molten aluminum filling smoothly, and no turbulence is seen, but the molten aluminum at the end of the die-casting is significantly lower than that at the front end, a local entrained air phenomenon is caused.

Figure 2.2 Temperature distribution after low-speed 0.3m/s casting is filled
② The temperature distribution of the filled casting is shown in Figure 2.2. The overall temperature of the casting is about 590°C, which is slightly higher than the liquidus line of the A380 material at 574.4°C. The risk of defects such as cold lab and surface flow marks on the casting is low.

Figure 2.3 Entrained air volume fraction after low-speed 0.3m/s casting is filled.
③Entrained air volume fraction of filled casting is shown in Figure 2.3. During the casting filling process, a small part of the entrained air remains in the casting area, and the casting has the risk of forming pores and bubbles.
3.Filling effect of casting at low pressure 0.5m/s.

Figure 3.1 Filling state of the low-pressure 0.5m/s shot chamber
① The molten aluminum in the shot chamber is shown in Figure 3.1.
The aluminum liquid filling the shot chamber stably, but the turbulence phenomenon occurs as soon as the aluminum liquid enters the runner, and the entrained air phenomenon is serious.
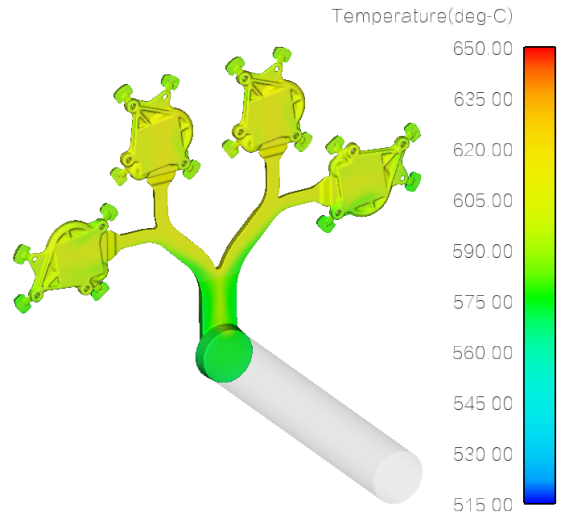
Figure 3.2 Temperature distribution after low-speed 0.5m/s castings are filled
② The temperature distribution of the filled casting is shown in Figure 3.2.
The overall temperature of the casting is about 610°C, which is higher than the liquidus line of A380 material at 574.4°C. With no defects such as cold lab and surface flow marks.
Figure 3.3 Entrained air volume fraction after low-speed 0.3m/s casting is filled
③ The distribution of Entrained air volume fraction after the casting is filled is shown in Figure 3.3.
There is more entrained air in the casting area during the filling process, with a higher risk of defects such as pores and bubbles.
4.Conclusion
①.The slower the low-speed, the less the volume of entrained air, but too low speed will reduce the temperature of the molten aluminum, and the casting will have problems occur such as cold lab and flow mark.
②.When the low-speed is too fast, the filling temperature of the casting is high, and the possibility of cold lab and flow marks is less, but the volume of entrained air will increase, and defects such as porosity and bubbles will appear.
③.To set the low speed, you must first determine the product requirements. If the casting is an appearance part, you can appropriately increase the low speed to avoid surface defects such as surface flow mark and cold lap to improve the surface molding quality. If the casting is air-tight, it is necessary to reduce the low speed as much as possible to ensure that the casting does not form a cold lap to achieve the best venting effect and ensure the casting sealing performance.
5. References
[1] A Concise Design Manual for Die Casting Molds / Edited by Huang Yong. --Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009.11



Comments