搜尋結果
39 items found for ""
- Mold Flow Simulation For Die Casting Mold
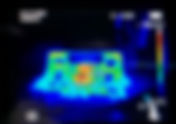
When you first get involved in casting, especially die casting, one of the very important steps in the design process is mold flow simulation. But why we do mold flow analysis and what is mold flow simulation? We will start with these two aspects and introduce the reasons and methods. High Pressure Die Casting Simulation The die casting process designer is a complex and empirical creative job. In die casting production, the three main elements are die casting machine, die casting alloy and die casting mold. The die casting process is the organic combination of these three elements and the reasonable choice of settings. Therefore, to die casting process parameters for the correct selection, control, and adjustment, so that a variety of process parameters to meet the needs of die casting production, in order to produce qualified die casting under other conditions of quality. CAE Technology Make use of the powerful computing and graphic functions of computers to assist mold design, improve the design accuracy and design reliability, design reasonable mold structure and reasonable pouring system. Numerical simulation of the die casting process by CAE technology, commonly known as computerized mold testing, visualizes the whole process of flow and solidification of metal liquid in the cavity during casting generation and analyzes the factors of defect formation. Mold Flow Simulation and Analysis With the continuous development of simulation technology, computer hardware, and software, The needs of the casting market, the numerical simulation of the casting process is to establish the correct mathematical models, and through the appropriate values, use the computer to analyze these models and use them to guide the casting practice in terms of flow, temperature, organization, etc. The simulation results are observed through post-processing, and the flow and solidification process of the metal fluid in the cavity is animated through multiple angles and profiles to track the view and locate the defective parts inside the casting. To support our customers in getting the best productivity and part quality, CAMEL always provides flow simulation by designing various kinds of runner layouts. By doing this our T1 success rate is over 96%. In this preliminary flow simulation, it appears that the outermost feeders are not supplying hot metal directly to problem areas while the center section is filling well. CAMEL adjusted the runner layout as shown below for a successful T1. Step 1: Eliminate (2) end feeders and make them overflow. Step 2: Change the feeder angle and gate towards the outer edge of the part. ABOUT CAMEL CORE BUSINESS: Aluminum Alloy Die Casting Mold Magnesium Alloy Die Casting Mold Zinc Alloy Die Casting Mold Trim Die(Mold) Milling & Turning Design & Prototyping CUSTOMERS MAIN INDUSTRIES: Automotive Telecom Equipment Mechanical Electrical Lighting Furniture Medical Instruments
- Improve Qualification Rate Of Die Casting Mold | Mold Manufacturing Process
The Concept Of Die Casting Mold Qualification Rate Die casting mold qualified rate is a system concept, from die casting machine edge, die casting initial inspection, cleaning, post-treatment, machining, transportation, and other aspects of the qualified rate belongs to the composition of die casting qualified rate, which is also called straight through rate. For example, the problem of equipment, the problem of mold, the problem of spraying, and so on, the problem of these points has a significant impact on the qualified rate of die casting machine edge, the failure of equipment and mold will increase the number of cold mold parts; the instability of equipment and mold will increase the number of defective products of automatic identification, the unreasonable heat balance of mold and spraying will increase the appearance defects of castings. Die casting machine edge waste is the biggest part of die casting qualified rate scrap proportion, and also one of the biggest hidden points of die casting cost. Today we will discuss the qualified rate refers to the qualified rate of machining, mold circles often said the qualified rate is generally referred to in this data. Machined casting material waste is still attributed to the defects of die casting, there are often defects: porosity, shrinkage, leakage, inclusions, deformation, black skin, bruising, etc. The most important defect is the problem of gas shrinkage and leakage, which is also the most difficult to solve and continues to repeat. Die casting pass rate of 95% is a value that can be reached, as long as the die casting company has the basic management process and standard, excellent mold tooling, plus an excellent die casting process and continuous improvement team, 95% of the die casting pass rate is not difficult to achieve, in the real production process there are many cases in the mold is good enough under the premise of 95% pass rate is easier to achieve. However 99% pass rate is another concept, this discussion is a symbolic value, it represents a higher, more sustainable, and stable pass rate standard, it may be 97%, may also be 99.7%, the ultimate requirement is how we can pursue to excellence, it is how to step by step reality. How Does A Die Casting Mold Company Need To Do To Achieve A 99% Compliance Rate? CAMEL mold manufacturing process includes the following ways Establish a project team A high-standard project team is led or vice-led by the top management. As a senior manager, you must personally lead the core team through a few typical projects and then work together to develop effective processes and standards. Goal setting It is important to set a high target pass rate according to the difficulty of the casting. Goal decomposition and division of responsibilities Goal decomposition and division of responsibilities are particularly important, most of the problems that arise later are caused by the lack of comprehensive and careful analysis in the early stage; most of the implementation is not in place because of unclear responsibilities. Therefore, for the division of responsibilities must be designated the relevant responsible person, we must have more than one person to discuss the basic knowledge of a responsible, each thing is ultimately responsible for only one person. To avoid the emergence of localism and empiricism, and to designate the corresponding project management personnel to supervise. Casting feasibility analysis - DFM (ideally simultaneous design) Casting feasibility analysis is the most basic work because now many casting design engineers do not understand die-casting, the design of the casting is difficult to fully meet the process of die casting. Die casting problems and effective communication with customers (to solve the difficulties or apply for relaxation of standards) The feasibility analysis report of the casting is done is actually just the beginning, how to communicate effectively with the customer is very important. Mold design (pouring system design, heat balance system design, mold flow analysis, structure design, DFMEA) If you want to design a pouring system with a high pass rate, you should use the idea of process compensation to design the pouring system, which may increase the cost of post-processing, but it is worthwhile. Design of thermal balance Thermal balancing systems require strong logistical support, mold repair resources, and management capabilities. Mold review (checklist check) All important nodes in the process need to do the review, the review of mold design is the top priority, the key problems of solution A and alternate measures program B. LINK TO: 1.What Is Die Casting Mold 2.Custom Die Casting In China 3.Die Casting vs Permanent Mold Casting 4.Steps Of Die Casting Die(HPDC Mold) DesignTechnical 5.Specifications Of Die Casting Dies 6.How Does Hot-chamber Die Casting Machine Work 7.How Much Does a Die Casting Tool Cost? 8.Mold Making & Die Casting Mold Manufacturing Process 9.How to Make Die Cast Molds
- How to Make Die Cast Molds?
The standardized mold production process is one of the core competitiveness in mold manufacturing. From mold order to mold output, it takes about dozens of steps; The key steps of making die cast molds organized are as follows. Order Preliminary Review → Final Mold Structure Review → Design Review Of Die Casting Mold; Design Review Of Trim Mold → Manufacturing Review → Mold Components Inspection; Mold Steel Hardness Inspection → Mold Base Inspection Report → Cavity & Core Inspection After CNC → Mold Electrode Inspection → Cavity & Core Inspection After Wire Cut → Cavity & Core Inspection After EDM → Mold Pre-Assembly Inspection → Trial Review → Sample Inspection Report → Die Casting Die Checking List → Trim Die Checking List; Inspection Qualified Notice Read More Details Design Review Of Die Casting Mold In the molding process, it is the Die that is key for productivity and part quality. Both precision and dimensional accuracy are needed to efficiently produce high-quality castings. Particularly during the casting process, the runner design and heat energy control prove to be essential factors for achieving the highest productivity and part quality. It is the CAMEL’s job to develop, and build dies that support best-in-class cycle-time, part quality, and die life. Tempering must be done before the mold trial to guarantee the die life. Before mold production, The design of die casting dies is also a top priority. We always do flow simulation by designing many kinds of runner layouts to get the best productivity and part quality. This way most of our die casting dies can be sampled successfully the first time. The preliminary flow simulation below appears to show that the overflow speed is too fast and may cause a high risk of mold flush issues. We reduced the area of overflow to control the speed and ensure a better cast and mold quality. Balanced Heat Energy CAMEL designs ample cooling lines to control the heat energy balance to get the best cycle-time and part quality. The balanced heat energy also lowers the risk of die cracking. Die Casting Parts Overflow is the essential factor for achieving the best part quality. We design all venting separately to ensure that venting can run smoothly and efficiently. This way parts will have a much lower risk of cold lap issues. Multi-cavity Trim Dies Trim dies are indispensable tools for high quantity production. Unprofessional mold makers need to adjust the multi-cavity trim die many times by welding. CAMEL designs all support blocks, cutters, guide pins, and guide bushes separately for each cavity. We also design separate locating components to control the runner deformation. This way most of our multi-cavity trim dies can be trimmed successfully the first time. LINK TO: 1. What Is Die Casting Mold 2. Custom Die Casting In China 3. Die Casting vs Permanent Mold Casting 4. Steps Of Die Casting Die(HPDC Mold) Design 5. Technical Specifications Of Die Casting Dies 6. How Does Hot-chamber Die Casting Machine Work 7. Mold Making & Die Casting Mold Manufacturing Process 8. How Much Does a Die Casting Tool Cost? 9. What is Mold Maintenance?
- What is Mold Maintenance?
The die casting mold‘s working environment is very harsh, especially since the mold cavity part is easily damaged. This leads to the die casting metal liquid drilling into these gaps, producing serious flying edges or even jammed sliding parts. These problems of die casting mold will cause casting defects, and even cause a lot of scraps. In order to ensure the quality of the die-castings and extend the service life of the mold, CAMEL recommends the die casting workshop to carry out mold maintenance work such as inspection and repair of the molds. Mold maintenance includes the following. Observation And Inspection Of The Mold There are 3 ways to check the mold, On-site inspection of the mold, that is, the mold repairer inspects the mold before it is used; The down-field inspection of the mold, that is, after producing a batch of castings, before the mold is put into storage, the mold repairer will check the condition of the mold; Weekly inspection of the mold, inspection, and maintenance cycle can generally be determined by the number of press shots, generally every 10,000 press shots, the need to remove the mold from the die-casting machine, disassemble the main parts for an inspection and maintenance work, the content of the following. (1) Observe the surface of the cavity to see if there are traces of strains and ablation of adhering metal chips, and polish the strains with abrasive cloth and polishing tools. (2) Observe all the top bar, core whether there is bending, cracking and fracture, if necessary, a copper or wooden hammer gently knocking check, bending, cracking and fracture of the Cores, projections, and top rods should be repaired or replaced immediately. (3) Check whether all the top bar is free to move in and out, whether there is a jamming phenomenon, the top bar hole and other mating surface drilled into the metal fluid, the top bar end surface is high, or lower than the mold surface. Problems found should be disassembled mold ejector parts for repair, the gap is too large for the top bar or sliding part to try to repair. (4) Use a magnifying glass to observe whether the surface of the cavity is cracked, cracks, scratches, and local collapse, and there are pits and barbs on the surface of the mold wall in the direction of the release. For minor mesh cracks on the surface of the cavity, they can be reinforced with a tungsten reinforcing machine and then polished. For larger cracks, collapses, and pits, the bottom metal must be removed and the mold steel welding rod must be used for welding (preferably with argon arc welding to ensure the welding quality). (5) Check if the exhaust system on the parting surface is clogged with grease or metal chips, and clean it up to ensure that the exhaust system is smooth. (6) Check whether the cooling system of the mold is smooth and free from blockage. Dimensional Accuracy Of Regular Identification Die casting mold use after a certain period of time will appear the naked eye can not detect the deformation and wear, thus affecting the dimensional accuracy of die-castings and make the processing volume change. Therefore, for the die-casting die with a high dimensional accuracy requirement, it is necessary to carry out the periodic identification of dimensional accuracy. The identification period is decided according to the specific requirements, the identification method can be used to periodically check the die casting or use three coordinate measuring instruments for measurement. Nitriding Treatment Die casting die after a certain period of time, the surface nitriding layer will be worn, thus reducing the surface hardness of the cavity, increasing the tendency of die casting sticky mold. For this reason, after every 30,000 die shots, the cavity should be disassembled, the surface should be polished and sent to the heat treatment workshop for nitriding treatment. Tempering Treatment Die casting die is used a certain number of times after the stress relief tempering treatment, According to improve the die casting die life of effective measures. Tempering temperature should be 30~50% lower than the original tempering temperature of die-casting material. During mass production, the aluminum residue is commonly found at the bottom of the mold, which needs to be cleaned up regularly to avoid mold collision. The stress-relieving tempering interval of aluminum alloy die casting mold is related to the die castings quality and the times of die casting shots, and usually: die casting mass less than 0.1kg, shots of 25000 times; die casting mass of 0.1kg-1kg, shots of 10000 times; When the casting mass is more than 1kg, shots of 5000 times. CAMEL deeply believes that good mold maintenance ensures a longer mold life and smooth production. Therefore, a quality mold must not only be stable during production but also easy to maintain. LINK TO: 1.What Is Die Casting Mold 2.Custom Die Casting In China 3.Die Casting vs Permanent Mold Casting 4.Steps Of Die Casting Die(HPDC Mold) DesignTechnical 5.Specifications Of Die Casting Dies 6.How Does Hot-chamber Die Casting Machine Work 7.How Much Does a Die Casting Tool Cost? 8.Mold Making & Die Casting Mold Manufacturing Process
- How Much Does a Die Casting Tool Cost?
The cost of a die casting tool has two main parts-mold and cavity processing. The cost of the tool is mainly controlled by the size of the die casting. The larger the part, the larger the tool and the higher the cost. The cost of machining the cavity is almost affected by all aspects of the part geometry. The Size Affects The Cost The main cost factor is the size of the cavity that must be processed, measured by the projected area and depth of the cavity. Any other elements that require additional processing will increase the cost, including the number of features, parting surfaces, edges, tolerances, and surface roughness. The Materials Affect The Cost The cost of the tool will be affected by the life of the die casting tool, and the life of the mold will be affected by the number of die castings and the materials we use. For example, a material with a high casting temperature, such as copper, will result in a short mold life. On the other hand, zinc can be cast at lower temperatures, which can lead to longer mold life. This effect will become more expensive as the number of production increases. The Side-cores Affect The Cost The last consideration is the additional cost for the side cores. However, the number of directions can limit the number of cavities that can be included in the mold. For example, a mold that requires 3 side core directions can only contain 2 cavities. There is no direct cost increase, but using more cavities may further save costs. Our capabilities CAMEL offer to die casting tool and high pressure die casting tool design; Our die casting tool solutions include tooling for aluminum, magnesium, and zinc die castings for complex products such as automotive components, medical equipment, and machinery parts industrial manufacturing. Accurate design and high-speed machining capabilities ensure superior die casting tool performance. LINK TO: 1, What Is Die Casting Mold 2, Custom Die Casting In China 3, Die Casting vs Permanent Mold Casting 4, Steps Of Die Casting Die(HPDC Mold) Design 5, Technical Specifications Of Die Casting Dies 7, How Does Hot-chamber Die Casting Machine Work 8, Mold Making & Die Casting Mold Manufacturing Process
- Glossary of Die Casting Terms
LINK TO: 1, Die Casting Process Design and Die Casting Process 2, Design points of the inner gates in the gating system for die casting mold 3, Working principle of the die casting mold 4, Structure, classification, and design of pouring/gating systems 5, Temperature controller for Die-casting Production 6, The CASINO Machine Parts in Bulgaria made by CAMEL Manufacture
- Die Casting Process Design and Die Casting Process
Die Casting Process Design Die casting process design is an important part of die casting production technology, mainly involving die casting process requirements for the shape and structure of the casting, the technical conditions of die casting (technical requirements), the process performance of die casting, and die casting parting surface determination. The Die-casting Process On The Requirements Of The Structure Of The Die Casting Die casting quality, in addition to the impact of various process factors, the structure of its parts process (reasonable) is also a significant factor, such as the location of the parting surface, the design of the gate, the layout of the launch mechanism, the accuracy of the guarantee, the type of defects. The type of defects and their degree, etc., are closely related to the structure of the die casting process itself (reasonable). Die casting structure affects the design of die casting mold structure and manufacture of difficulty, production efficiency and service life, and other aspects. The reasonable die-casting structure can shorten the product trial period, reduce production costs, ensure product quality, improve production efficiency. Therefore, the die casting shape structure should strive to be simple, especially to eliminate the inability or difficulty of lateral core extraction of the internal side concave, simplify the mold structure, and improve the service life of the mold. The main issues to consider when designing the structure of die casting are as follows: To help simplify the mold structure, extend the life of the mold 1) castings at the parting surface should try to avoid rounded corners Rounded corners increase the mold's processing difficulty and make the rounded corners of the mold strength and life have decreased. If the dynamic mold and fixed mold are slightly misaligned, die-casting rounded part of the easy form a step The appearance will be affected. If the structure changes to a flat shape, the parting surface is flat and easy to process, avoiding the above shortcomings. 2) to avoid internal side concave Die casting internal flange and bearing hole for the internal concave structure, core extraction difficulties, the need to set a complex core extraction mechanism or fusible core. As a result, it increases the complex shape of the mold and processing volume and reduces production efficiency. However, if the inner concave structure changes to a non-internal concave structure, the difficult core extraction can be solved, and the mold structure can be simplified. 3) Avoid crossed inaccessible Crossed not through the hole must use a higher tolerance fit of each other crossed cores, increasing the amount of mold processing and strict control of the order of core extraction. Once the metal liquid is in the gap of the crossed cores, it will make the core extraction difficult. If the crossed not through the hole to avoid crossing the inaccessible structure, you could avoid the core's cross, eliminating the shortcomings mentioned above. 4) to avoid partial thinning of the mold Casting structure because the hole edge from the flange distance is too small, easy to make the mold insert fracture. If the die casting to a local ≥ 3mm structure, the insert can be made with sufficient strength, thereby improving the service life of the mold. Conducive to reducing the extraction of core parts, improve the structure of the mold Reduce the parting surface is not perpendicular to the core part, reduce the complexity of the mold, and ensure the accuracy of die castings. The depth of the square hole in the center of the die casting is deep, the core distance is long, requiring a special core extraction mechanism, the mold is complex; plus the cantilever core into the cavity, easy to deform, difficult to control the sidewall wall thickness uniform. The use of an H-shaped section structure does not require core extraction, simplifying the mold structure. Conducive to core extraction, convenient casting mold release Die casting structure due to the core by the tab obstruction can not be smoothly extracted core. If the shape of the die casting suitably modifies to a structure conducive to core extraction, when can smoothly extract the core. LINK TO: 1, Design Of The Cross Sprue 2, Design points of the inner gates in the gating system for die casting mold 3, Working principle of the die casting mold 4, Structure, classification, and design of pouring/gating systems 5, Temperature controller for Die-casting Production 6, The CASINO Machine Parts in Bulgaria made by CAMEL Manufacture
- Design Of The Cross Sprue
The cross sprue is the passage from the end of the straight sprue to the front of the inner gate; sometimes, the cross sprue can separate into the main cross sprue and the transition cross sprue. The Cross Sprue Should Conform To The Following Requirements 1) Providing a stable flow of metal fluid. 2) Providing less resistance to the flow of the metal fluid. 3) Low amount of gas encapsulated in the metal fluid during the flow. 4) Provide suitable conditions for the heat balance of the cavity. 5) Make the metal liquid have a suitable solidification time, not hinder the transfer of complementary shrinkage pressure, and not extend the cycle of die-casting. 6) Heat loss should be minimized when the metal liquid flows through the cross sprue. The Layout Of Multi-cavity Cross Sprue The production of large and complex die casting, mainly using single-cavity die casting dies. While the shape of the simpler small dies casting and the production batch is more significant, to improve the efficiency of die casting production, reduce the total mold cost. Usually, using multi-cavity die casting dies. Multi-cavity die casting mold cavities can set the same but also can select different types. A mold multi-cavity die casting mold layout form of the cross sprue should be depending on the layout of each cavity. The structure of the multi-cavity position should base on the structural characteristics of each die casting, the flow condition of the metal liquid, and the heat balance of the mold temperature so that each cavity of the die casting process conditions as far as possible to achieve consistent. The Layout Forms Of Multi-cavity Cross Sprue Are Rough As Follows 1) Straight-line arrangement In general, when the metal press into the sprue, the metal liquid starts to divide, and the mainstream of the metal liquid flows forward. In contrast, a small stream of metal liquid flows from the transition cross sprue into the nearest cavity under a slight overpressure to form a pre-filled state. This situation repeats—the results in a small amount of fluid flowing into each cavity. When the mainstream of liquid metal reaches the front of the central cross sprue, the corresponding impact pressure generates, and the cavities fill in turn from top to bottom. Because the pre-filled metal liquid is in a minimal force into the cavity, and in an instant, its temperature will have a significant reduction or even close to the cooling state when they are not easy to fuse with the later entry of the mainstream metal liquid. This filling time difference will make the die casting molding effect reduce; close to the direct sprue die castings are usually easy to produce die-casting defects. 2) Symmetrical arrangement Symmetrically arranged cross sprue could use for larger die castings. The metal liquid pressed in from the straight sprue enters the cavity through the evenly bifurcated cross sprue. It can ensure that the double cavities have the same die casting process conditions, the mold body is also more balanced force. 3) Comb-style arrangements The comb arrangement cross sprue has the characteristics of the comb inner gate and the T-shaped cross sprue. 4) Surrounding arrangement The layout of each cavity is the same as the distance of the straight sprue; the cross sprue can arrange in the form of surround. This arrangement makes the metal liquid flow into each cavity under the same die casting condition, satisfying the principle of filling and cooling simultaneously. 5) Other forms of arrangement Depends on the structure of die casting, the layout of the multi-cavity mold cavity and the cross sprue also varies. The arrangement of the cross sprue is generally flat and branching, oblique branching, and circular branching. In practice, it depends on the structural characteristics of the die casting. What Are The Key Factor For Productivity And Part Quality? In the Die casting process, It is the Die that is key for productivity and part quality. Not only precision and dimensional accuracy is needed to produce high-quality castings efficiently. Especially in the casting, runner design and heat energy control prove to be essential factors for achieving the highest productivity and part quality. The CAMEL's job is to develop and build dies that support best-in-class cycle-time, part quality, and die-life. Tempering must be done before the mold trial to guarantee the die-life. LINK TO: 1, Structure, classification, and design of pouring/gating systems 2, Maintenance of die casting mold 3, Working principle of the die casting mold 4, Mold debugging 5, Temperature controller for Die-casting Production 6, The CASINO Machine Parts in Bulgaria made by CAMEL Manufacture
- Design Points Of The Inner Gates In The Gating System For Die Casting Mold
Determination Of The Cross-sectional Area Of The Inner Gates The cross-sectional area of the gates directly determines the inner gates' speed and filling time. When the inner gates speed is selected, if the cross-sectional area of the inner gates, If the cross-sectional area of the gate is too large, the metal liquid fills the cavity too fast, so that the gas in the cavity is not discharged in time to produce pores and other die casting defects. If the cross-sectional area of the inner gates is too tiny, it prolongs the filling time, and in the filling process, part of the metal liquid cools too fast, resulting in the cavity filling is not satisfied with the phenomenon. In order to obtain the ideal filling time, the inner gates cross-sectional area remains unchanged, adjust the action on the liquid metal pressure and pressure injection punch speed, can also change the liquid metal filling time, but the adjustment range is minimal, in addition, to consider the bearing capacity of the die-casting machine. Therefore, in the design process, predetermine the inner gates' cross-sectional area is a critical design content. At present, in die casting practice, is the metal liquid at a certain speed and predetermined time to fill the cavity is the primary basis of calculation. Design Of The Thickness Of The Inner Gates In the inner gates cross-sectional area, the thickness of the inner gates has a more significant impact on the formation of a good filling flow state. Therefore, it is appropriate for thin-walled complex die castings to use thin inner gates to ensure the necessary speed of the inner gates. However, when the inner gate thickness is too thin, the metal liquid flow of tiny impurities, such as segregation, inclusions, oxides, and other impurities, will lead to local blockage of the inner gates, reducing the effective flow area of the inner gates. At the same time, the metal liquid entering the cavity is easy to produce an atomization phenomenon, thus blocking the exhaust channel, and then wrap the gas in the cavity to produce die casting defects. When the thickness of the inner gates is thicker, it helps to reduce the filling speed. At the same time, the inner gate's solidification time is the almost quadratic increase in the thickness of the inner gates, which is conducive to the transfer of the complementary shrinkage pressure. Therefore, without affecting the surface of die casting without increasing the cost of removing the inner gates, the thickness of the inner gates can be increased as much as possible. The width of the inner gates should also be selected appropriately, and the width is too large or too small will cause the metal liquid to rush straight to the opposite side of the wall, resulting in vortex flow to wrap the air and impurities and produce scrap. The length of the inner gates directly affects the quality of the casting. If the inner gates are too long, it will affect the pressure transfer, cooling, and casting surface will be easy to form a cold partition pattern. If the inner gates are too short, the temperature at the inlet will rise quickly and speed up the wear of the inner gate, and it is easy to produce a spraying phenomenon. Key Points For The Design Of The Position Of The Inner Gates When designing the inner gates, the most crucial thing is determining the inner gates' location, form, and direction. According to the shape and structure characteristics of die casting, wall thickness change, shrinkage deformation, and mold parting surface, and other factors, the flow pattern and filling speed change of metal liquid in the filling, as well as the expected filling process, may appear in the dead corner area, wrapped gas and complex partition parts, and arrange the appropriate overflow and exhaust system. CAMEL is a professional (HPDC) high-pressure die-casting dies manufacturer. Our design team specialized in Design, build, and production within over ten years of stable die casting tool and die manufacturing experience. Contact us if you have any die casting mold problems in all industries. LINK TO: 1, Structure, classification, and design of pouring/gating systems 2, Maintenance of die casting mold 3, Working principle of the die casting mold 4, Mold debugging 5, Temperature controller for Die-casting Production 6, The CASINO Machine Parts in Bulgaria made by CAMEL Manufacture
- Structure, Classification, And The Design Of Pouring/Gating Systems
The metal die casting mold pouring system is the channel to fill the die cavity with the molten metal liquid inside the die casting machine press at high temperature, high pressure, and high speed. Gating System And Types It includes straight sprue, cross sprue, inner gate, and overflow exhaust system. In the process of guiding the metal liquid to fill the cavity, they play an important role in controlling and regulating the flow state of the metal liquid, the speed and pressure transfer, the exhaust effect, and the heat balance state of the die casting mold, etc. Therefore, the pouring system is an important factor in determining the surface quality of the die casting and the internal microstructure state. At the same time, the pouring system has a direct impact on the efficiency of die casting production and the life of the mold. The design of the pouring system is an important part of the die casting mold design; it is necessary to analyze the structural characteristics of the die casting from the theoretical point of view, but also to have the practical experience of the application of the die casting process. Therefore, the design of the pouring system must take the method of combining theory and practice. 1. The structure of the pouring system The channel where the metal liquid fills the cavity under pressure is called the pouring system. The pouring system is mainly composed of straight sprue, cross sprue, and internal gates. According to the form of die-casting machine and the introduction of metal liquid casting mold casting system composition form also has not hot room, vertical cold room, all vertical and horizontal cold pressure chamber several. 2. The main content of design of the pouring system ① according to the die casting size, quality (weight), and the positive projection area on the parting surface, and according to the actual situation of the field equipment, selected the type of die casting machine used, model, and diameter of the chamber. When the choice of vertical cold chamber die casting machine or hot chamber die casting machine, but also choose the appropriate nozzle so that the nozzle shape and pouring system to adapt. ② die casting dimensional accuracy, surface and internal quality requirements, bearing load conditions, pressure resistance, sealing requirements, etc., in order to carry out a comprehensive analysis to determine the location of the metal liquid into the cavity direction and flow state. ③Analysis of the complexity of the die casting, structural characteristics, and processing datum, combined with the selection of parting surface, determine the overall structure of the pouring system and the main dimensions of each component. ④Analyze the flow of metal liquid and determine the position of the overflow tank and exhaust channel. ⑤ Determine the suitable mold temperature adjustment measures according to the influence of the metal liquid flow on the mold temperature. Design Of Inner Gates The inner gate is a section of the sprue from the end of the cross sprue to the cavity, which is a channel to guide the molten metal liquid to fill the molding cavity at a certain speed, pressure, and time. The function of the inner gate is to introduce the metal liquid into the cavity in the best flow state according to the structure, shape, and size of the die casting to obtain a high-quality die casting. Therefore, when designing the inner gates, the main purpose is to determine the location and direction of the internal gate and the cross-sectional size of the inner gates, to anticipate the flow state of the metal liquid during the filling process, and to analyze the possible dead corner area or the air wrapping area, so as to set up effective overflow and exhaust slots in the appropriate areas. Since there are many factors affecting the internal gate, it has the greatest influence on the quality of die casting, so there are many design options. CAMEL is a professional (HPDC) high-pressure die casting dies manufacturer. Our design team specialized in the design, build, and production within over ten years of stable die casting tool and die manufacturing experience. Contact us if you have any die casting mold problems in all industries. LINK TO: 1, What is die casting? 2, What is die casting mold? 3, Steps Of Die Casting Die(HPDC Mold) Design 4, Glossary of die casting terms 5, How to choose steel for die casting mold? 6, How to Extend the Life of Die-casting Tools? 7, Failure Mode and Analysis Of Die-casting Dies 8, How to choose a die casting machine? 9, How does the cold-chamber machine work? 10, How does the hot-chamber machine work?
- Process Characteristics Of Aluminum Alloy Die Casting (Cold-Chamber Die Casting)
1. According to the principle of fluid mechanics, the theoretical analysis and some calculations of the movement of liquid metal in the pressure chamber of the horizontal cold-chamber die casting machine are based on the analysis that: the slow injection process of the horizontal cold chamber die casting machine punch is accelerated The combination of motion and uniform motion, the result of the combination directly affects the quality of die castings. The amount of air that the liquid metal is involved in the pressure chamber is related to the slow injection acceleration, slow injection speed, initial fullness, and pressure chamber diameter, and there is a critical slow injection speed and optimal acceleration, where the speed and acceleration It can minimize the amount of air involved and minimize the porosity of castings. 2. The filling process of liquid metal during die casting is a process in which many contradictory factors are unified. Among the many factors affecting filling, mainly pressure, speed, temperature and time, etc., time is the result of the coordination and synthesis of related process parameters, and each process factor influences and restricts each other, adjust a certain process Factors, it will inevitably cause the corresponding process factors to change, and may in turn affect the adjusted process factors to cause changes. Therefore, only by correct selection, control and adjustment of these process parameters, so that the various process parameters meet the needs of die casting production, can it be guaranteed that qualified die casting parts can be produced under other good conditions. 3. The basic characteristics of aluminum alloy die casting are filling under high pressure and high speed, and crystallization under high pressure. During the entire rapid injection stage, the molten metal enters the cavity in the form of a jet at a speed of 30 to 60 m/s, and the molten metal does not envelop the gas. It is impossible. In this case, by adjusting the process parameters and the process plan, the key is where and in what form the pores are distributed reasonably. Because the high-pressure jet breaks the gas into dispersed small pores and remains in the casting, the strength cannot be improved by heat treatment, and the elongation of the die casting is low. Therefore, die casting is generally suitable for the production of thin-walled shells and outer covers that do not need to bear large impact loads, and is not suitable for manufacturing important safety components. 4. According to the process characteristics of aluminum alloy die casting, it is difficult to form thin-walled large areas. If the wall thickness is too large or severely uneven, defects and cracks are easy to occur. It is hoped that the wall thickness of the die casting parts will be as uniform as possible. For large aluminum alloy die casting parts, Generally, the wall thickness should not exceed 6mm. Under normal process conditions, the wall thickness of die castings should not exceed 4.5m. The thickness of the die casting At the wall, in order to avoid shrinkage and other defects, the wall thickness should be reduced and reinforced ribs should be added. 5. Due to the characteristics of the aluminum alloy die casting process, the alloy used requires a small crystallization temperature range, a small thermal cracking tendency and a small shrinkage coefficient. 6. It is a feature of die casting process to be able to cast relatively deep holes well. For some holes with low precision requirements, they can be used directly without machining, thus saving machining man-hours. There is a certain relationship between the diameter and depth of the die cast hole on the part, and the smaller hole can only be die cast to a shallower depth. Generally, the hole diameter is not less than 2mm, and the hole depth is not more than 4~8 times the hole diameter. The threaded holes on the castings are often die cast to meet the requirements of the core hole, and then processed (mostly tapping) to make the threaded hole. 7. At the junction of the die casting wall and the wall, whether it is a right angle, an acute angle or an obtuse angle, it should be designed to be rounded. In order to facilitate the removal of die castings from the cavity and core of the mold, prevent surface scratches, and extend the life of the mold, the die castings should have a reasonable draft angle. Its size depends on the wall thickness of the casting and the type of alloy. The thicker the wall thickness of the casting, the greater the tightness of the alloy to the core, and the greater the draft angle. The greater the shrinkage of the alloy, the higher the melting point, and the greater the draft angle. In addition, the inner surface of the casting or the inner wall surface of the hole has a larger draft angle than the outer surface. Within the allowable range, a larger draft angle should be used to reduce the required pushing force or core pulling force. Generally, the draft angle is 0.5°-1.5. 8. In die casting process, threads can be directly die cast under certain conditions. 9. Various embossing, netting, text, signs and patterns can be die cast on die casting. 10. Metal or non-metal parts (inserts) can be embedded in the die casting mold first, and then cast together with the die casting parts. This can make full use of the properties of various materials (such as strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, magnetic permeability, conductivity, etc.) to meet the requirements for use under different conditions, and it can also make up for the poor processability of the casting structure. The lack of point, and solve the die casting problem of parts with special technical requirements. 11. Die castings have precise dimensions and good casting surfaces, and generally do not need to be machined. At the same time, due to the existence of internal pores in die casting, mechanical processing should be avoided as much as possible. However, after all, the die cast parts cannot be directly assembled and used in any situation. Therefore, in some cases, some surfaces or the parts are machined. The surface layer of the die casting is dense and uniform, with good mechanical and physical properties. The thickness of this surface layer is about 0.5~0.8mm, so the general machining allowance is preferably 0.3~0.5mm.
- Maintenance Of Die Casting Mold
The Purpose Of Maintenance And Maintenance Of Die Casting Mold 1) The mold can maintain the best performance state and ensure normal production. 2) Extend the service life of the mold. Daily maintenance and maintenance methods of the die casting mold Whether the running mold is in a normal state 1) Whether the mechanism is operating normally and whether there are any wearing parts that need to be replaced. 2) Are the movable parts such as the guidepost, ejector rod, and row position worn and well lubricated? It is required to add high-temperature lubricating oil at least once per shift, and the special structure should increase the number of refueling. 3) Whether the sprue bushings and shunt cones are worn. 4) Clear the front of the slider (row position) position. Normal production conditions Check whether the defects of the product are related to the mold. A comprehensive inspection of the mold and anti-rust treatment should be carried out when the machine is off 1) Clean the mold face, clean the mold, especially the cavity. 2) Check the mold. If the parts or parts are damaged, make a record for replacement or repair. 3) Wipe dry the moisture in the cavity, core, ejector mechanism, and row position, and spray mold anti-rust agent or apply butter. The molds after getting off the machine for inspection should be placed in the designated place, and the specific conditions should be recorded and kept in the designated area. 1) Open the mold and check the internal anti-rust effect. If there is any abnormality, the anti-rust treatment must be performed again; the mold that is not used for a long time must be coated with butter. 2) Place the mold to be repaired in the area to be repaired, and store it in the storage area for standby after the repair is completed. 3) Regular mold maintenance: ①The mold needs to be tempered to relieve stress after wire cutting; ②After the mold trial is completed, it needs to be tempered before mass production; ③The mold needs to be tempered to relieve stress after using 5000 molds. 10000 molds, 20000 molds, follow-up can be tempered according to the situation; ④Other surface strengthening treatments (such as nitriding, etc.) can be treated at the same time during tempering according to the situation; ⑤Part replacement. 4) Routine inspections every season It mainly cleans and maintains molds that have not been used for more than two months. Put it back in place and make inspection records. Maintenance precautions 1) Non-professional maintenance personnel or without the permission of professional maintenance personnel can not dismantle the mold for maintenance. 2) A minor failure in the production process can be solved by the adjuster according to the situation, such as ①When the product sticks to the mold, Use a copper needle to knock out at the feed nozzle, do not use steel needles and other hard objects to hit the mold, such as burning with fire, be careful not to damage the surface of the mold; ②The cavity is slightly scratched, and the polishing material can be selected according to the finish of the cavity. Do not use sandpaper and other polishing materials, which should be done by professional maintenance personnel. 3) Professionals should not change the structure at will when repairing the mold, and the structure must be changed after the approval of the quality engineering department. 4) Ensure the quality of maintenance, select appropriate equipment, materials, tools, and methods to solve the problem, and complete it as quickly as possible. 5) The maintenance of the mold requires a record for easy traceability.